Table of Contents
The locate is a command line utility for finding files by name in Linux, just like find command. However, it works more efficiently compared to its counterpart; it uses one or more databases populated by the updatedb program and prints file names matching at least one of the patterns (a user provides) to standard output.
Locate package is provided by the GNU findutils or mlocate packages. These packages are known to provide the same implementation of the program. On most CentOS/RHEL systems, findutils comes pre-installed, however, if you try to run a locate command, you may encounter the error:
How to install mlocate on Linux
1. To install mlocate, use the YUM or APT package manager depending on your Linux distribution as shown.
sudo yum install mlocate [On CentOS/RHEL]
sudo apt install mlocate [On Debian/Ubuntu]2. After installing mlocate, you need to update the database for mlocate, which is used by locate command as root user with the sudo command, otherwise you will get an error.
sudo updatedbThe default database storage location is /var/lib/mlocate/mlocate.db.
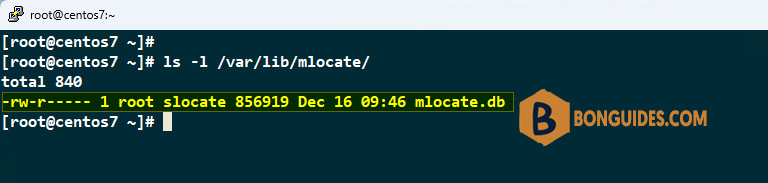
Once the database is updated, now try to run the locate command, which should work this time around.
locate php.iniTo find an exact match according to pattern you enter, use this -b option and the \ globbing option as in the following syntax.
locate -b '\php.ini'






