Table of Contents
Windows Subsystem for Linux
The Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) lets developers run a GNU/Linux environment — including most command-line tools, utilities, and applications — directly on Windows, unmodified, without the overhead of a traditional virtual machine or dualboot setup. Below is the list of Linux distributions that supported by WSL for auto installation.
PS C:\> wsl -l -o
The following is a list of valid distributions that can be installed.
Install using 'wsl.exe --install <Distro>'.
NAME FRIENDLY NAME
Ubuntu Ubuntu
Debian Debian GNU/Linux
kali-linux Kali Linux Rolling
Ubuntu-18.04 Ubuntu 18.04 LTS
Ubuntu-20.04 Ubuntu 20.04 LTS
Ubuntu-22.04 Ubuntu 22.04 LTS
OracleLinux_7_9 Oracle Linux 7.9
OracleLinux_8_7 Oracle Linux 8.7
OracleLinux_9_1 Oracle Linux 9.1
openSUSE-Leap-15.5 openSUSE Leap 15.5
SUSE-Linux-Enterprise-Server-15-SP4 SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 SP4
SUSE-Linux-Enterprise-15-SP5 SUSE Linux Enterprise 15 SP5
openSUSE-Tumbleweed openSUSE TumbleweedAt this moment, WSL doesn’t support Ubuntu 23.04 officially. So, we need to install it manually. Below is a quick snapshot about the manual process.
- Install an Ubuntu 22.04 instance on WSL.
- Install Docker on the Ubuntu instance.
- Pull the Ubuntu 23.04 image from Docker Hub.
- Create a container from Ubuntu 23.04 image.
- Export the container to a .tar file.
- Import the exported .tar file to an instance on WSL.
Before you begin
To install Ubuntu 23.04 on WSL, make sure you have:
Install the Ubuntu Instance
By default, when enabling WSL on Windows 10/11. The Ubuntu 22.04 is being installed automatically. If it not, you can install it using the below command.
wsl --install ubuntuTo get this list of the installed instances on your system, run wsl -l -v.
PS C:\> wsl -l -v
NAME STATE VERSION
* Ubuntu Stopped 2
Debian Running 2To start the Ubuntu instance, run wsl -d ubuntu. One the instance starts, you would navigate to the bash of the Ubuntu instance automatically.
PS C:\Users\admin> wsl -d ubuntu
To run a command as administrator (user "root"), use "sudo <command>".
See "man sudo_root" for details.
Welcome to Ubuntu 22.04.2 LTS (GNU/Linux 5.15.90.4-microsoft-standard-WSL2 x86_64)
* Documentation: https://help.ubuntu.com
* Management: https://landscape.canonical.com
* Support: https://ubuntu.com/advantage
This message is shown once a day. To disable it please create the
/home/bonben/.hushlogin file.
bonben@DESKTOP-K34B7Q9:/mnt/c/Users/admin$Install Docker on Ubuntu instance
1️⃣ You can install Docker on the Ubuntu 22.04 instance following the Docker’s documentation from this link. Or you can simply run the below script to install it automatically.
sudo wget -qO - https://bonguides.com/docker | bashWhen the installation finishes, you can see the docker service is running.
● docker.service - Docker Application Container Engine
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/docker.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Thu 2023-09-21 13:47:33 +07; 319ms ago
TriggeredBy: ● docker.socket
Docs: https://docs.docker.com
Main PID: 1863 (dockerd)
Tasks: 12
Memory: 30.8M
CGroup: /system.slice/docker.service
└─1863 /usr/bin/dockerd -H fd:// --containerd=/run/containerd/containerd.sock2️⃣ Pull the Ubuntu 23.04 image from Docker Hub
sudo docker pull ubuntu:lunar#Output
lunar: Pulling from library/ubuntu
10fb01f4f619: Pull complete
Digest: sha256:f1090cfa89ab321a6d670e79652f61593502591f2fc7452fb0b7c6da575729c4
Status: Downloaded newer image for ubuntu:lunar
docker.io/library/ubuntu:lunar3️⃣ Get the list of your docker images.
sudo docker images#Output
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
ubuntu lunar 21098a29e034 5 weeks ago 70.3MBCreate and export a docker container
Once you have the image of Ubuntu 23.04. In the next steps, you can create a docker container from it then export the container for WSL.
1️⃣ From the Linux shell, run the below command to create a container from the Ubuntu 23.04 image the go to the shell of the container.
sudo docker run -it --name ubuntu23 ubuntu:lunar2️⃣ As you can see below, when the container is created, the prompt change from the Linux shell (on WSL) to the container shell (on docker). From here, you can check the version of the Ubuntu container.
bonben@DESKTOP-K34B7Q9:/mnt/c/Users/admin$ sudo docker run -it --name ubuntu23 ubuntu:lunar
root@4dbae163af51:/# cat /etc/os-release
PRETTY_NAME="Ubuntu 23.04"
NAME="Ubuntu"
VERSION_ID="23.04"
VERSION="23.04 (Lunar Lobster)"
VERSION_CODENAME=lunar
ID=ubuntu
ID_LIKE=debian
HOME_URL="https://www.ubuntu.com/"
SUPPORT_URL="https://help.ubuntu.com/"
BUG_REPORT_URL="https://bugs.launchpad.net/ubuntu/"
PRIVACY_POLICY_URL="https://www.ubuntu.com/legal/terms-and-policies/privacy-policy"
UBUNTU_CODENAME=lunar
LOGO=ubuntu-logo3️⃣ Type exit then hit Enter to exit the shell of the container to go back to the shell of the Linux instance (on WSL). See below for details.
root@4dbae163af51:/# exit
exit
bonben@DESKTOP-K34B7Q9:/mnt/c/Users/admin$4️⃣ Now, run docker ps -a on the Linux instance to get the list of the docker containers. You should see the container that created in the step 2.
sudo docker ps -a#Output
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
4dbae163af51 ubuntu:lunar "/bin/bash" 4 minutes ago Exited (0) About a minute ago ubuntu235️⃣ This is time for exporting the Ubuntu 23.04 container to a .tar file. Below command will export the container named ubuntu23 to /tmp/ubuntu23.tar.
sudo docker export ubuntu23 > /tmp/ubuntu23.tarYou can check the file has been exported by the ls command.
bonben@DESKTOP-K34B7Q9:/mnt/c/Users/admin$ ls -l /tmp/
total 71084
drwx------ 2 root root 4096 Sep 21 13:35 snap-private-tmp
-rw-r--r-- 1 bonben bonben 72775168 Sep 21 14:17 ubuntu23.tar6️⃣ From the Windows host, you can see the exported file using the Windows Explorer as below. Everything is ready, you can continue to the last section.
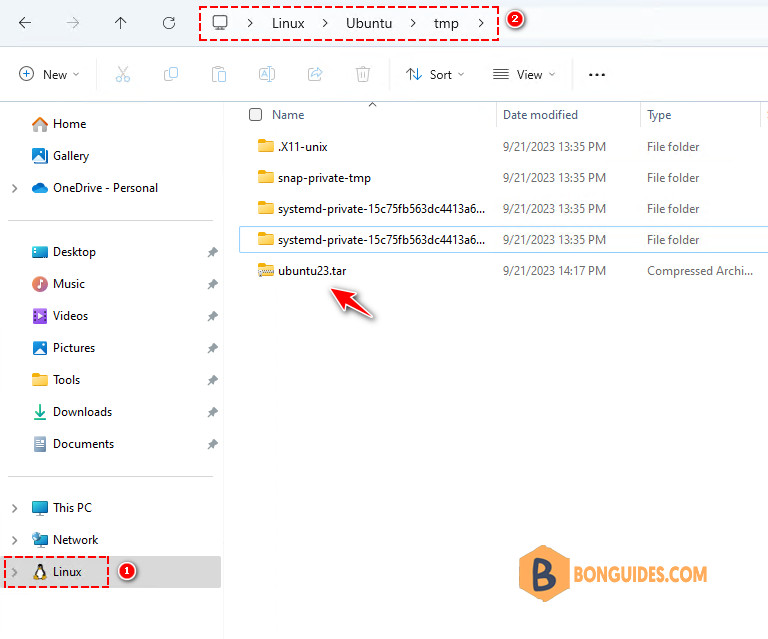
Import .tar file as a WSL instance
We’re nearly done, in the next steps we need to:
1️⃣ Create some new folders for the WSL instance. You can create the folders manually using File Explorer or you can open a new PowerShell window then run the below command.
New-Item D:\WSL, D:\WSL\temp, D:\WSL\ubuntu23 -Type Directory2️⃣ In the Windows host, copy the exported tar file from the Ubuntu instance to the folder D:\WSL\temp.
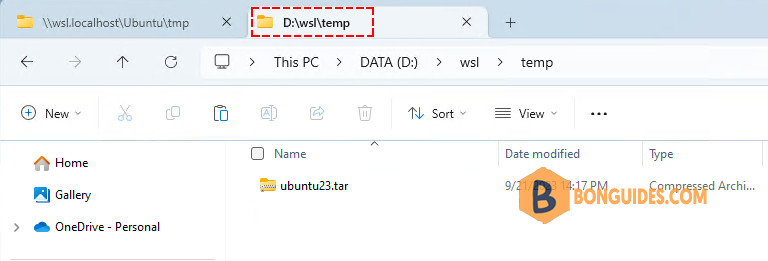
3️⃣ From Windows PowerShell (not the Linux shhell), run the following command to import the tar file as a WSL instance.
wsl --import ubuntu23 'D:\WSL\ubuntu23' 'D:\WSL\temp\ubuntu23.tar'
4️⃣ Run wsl -l -v in PowerShell to verify the instance has been created.
PS C:\> wsl -l -v
NAME STATE VERSION
* Debian Stopped 2
ubuntu23 Stopped 2
Ubuntu Running 25️⃣ Run the Ubuntu 23.04 instance with wsl -d ubuntu23 command.
PS C:\> wsl -d ubuntu23
root@DESKTOP-K34B7Q9:/mnt/c# cat /etc/os-release
PRETTY_NAME="Ubuntu 23.04"
NAME="Ubuntu"
VERSION_ID="23.04"
VERSION="23.04 (Lunar Lobster)"
VERSION_CODENAME=lunar
ID=ubuntu
ID_LIKE=debian
HOME_URL="https://www.ubuntu.com/"
SUPPORT_URL="https://help.ubuntu.com/"The virtual disk of the instance should be created in D:\WSL\ubuntu23.
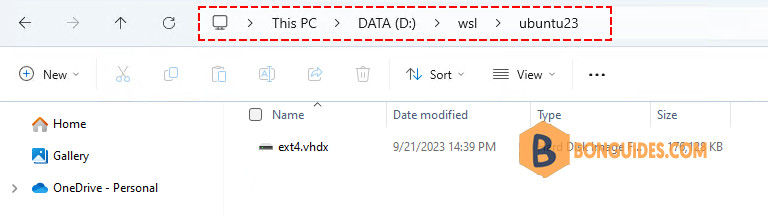
Conclusion
This post shows the way to create an unsupported Linux distribution on WSL using docker. Using this method, you can create any Linux distributions on WSL if they’re supported by Docker.
Not a reader? Watch this related video tutorial:





