Table of Contents
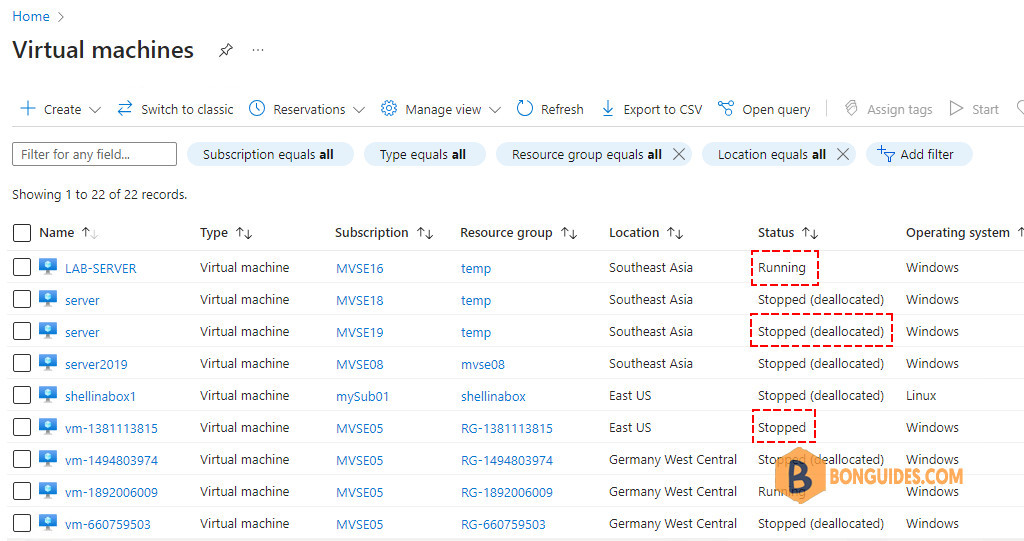
Even when stopped, Azure VMs that are not deallocated continue to incur costs. This article explores methods to find the stopped Azure VMs and deallocating them.
Find Stopped Azure VMs with PowerShell
When an Azure VM is shutdown using the operating system it enters a “stopped” state. In this state, the server is not running but the compute resource is still being held by Azure so you continue to get charged for that compute. Virtual Machines should be deallocated by either stopping them in the Portal or using a PowerShell Stop-AzVM cmdlet.
PowerShell can be used to look up the power state of VMs in your Azure Subscription as follows:
$array = @()
foreach ($vm in Get-AzVM) {
$object = New-Object -TypeName PSObject -Property $([ordered]@{
VMName = $vm.Name
PowerState = (Get-AzVM -VMName $($vm.Name) -Status).PowerState
ResourceGroup = $vm.ResourceGroupName
})
$array += $object
}
$arrayThe results might look like below.:
- The virtual machine vm-1162587192,power state is ‘VM deallocated‘. We’ll not be charged for this VM because it’s deallocated.
- The virtual machine vm-1555300244 power state is ‘VM Stopped’. It’s not deallocated, so we continue to get charged for that compute even it has been stopped.
VMName PowerState ResourceGroup
------ ---------- -------------
vm-1162587192 VM deallocated RG-1162587192
vm-1185303510 VM running RG-1185303510
vm-1555300244 VM stopped RG-1555300244
vm-210251813 VM running RG-210251813We want to find the stopped VM (without deallocated). So, we use the Where-Object cmdlet to filter for those that are stopped but not deallocated.
$array = @()
foreach ($vm in Get-AzVM) {
$object = New-Object -TypeName PSObject -Property $([ordered]@{
VMName = $vm.Name
PowerState = (Get-AzVM -VMName $($vm.Name) -Status).PowerState
ResourceGroup = $vm.ResourceGroupName
})
if (($object.PowerState -eq "VM stopped")) {
$array += $object
}
}
$arrayVMName PowerState ResourceGroup
------ ---------- -------------
vm-1555300244 VM stopped RG-1555300244Finally, we can proceed to properly shut down those VMs and deallocate their resources. The below script will find all stopped VMs then deallocating them.
$array = @()
foreach ($vm in Get-AzVM) {
$object = New-Object -TypeName PSObject -Property $([ordered]@{
VMName = $vm.Name
PowerState = (Get-AzVM -VMName $($vm.Name) -Status).PowerState
ResourceGroup = $vm.ResourceGroupName
})
if (($object.PowerState -eq "VM stopped")) {
$array += $object
}
}
$array
foreach ($stopedVM in $array) {
Write-Host "Stopping VM $($stopedVM.VMName)" -ForegroundColor Yellow
Stop-AzVM -Name $($stopedVM.VMName) -ResourceGroupName $($stopedVM.ResourceGroup) -Force
}As you can see, the power state of the VM was changed from ‘VM stopped‘ to ‘VM deallocated‘. It means you will not be charged for the VM anymore.
VMName PowerState ResourceGroup
------ ---------- -------------
vm-1162587192 VM deallocated RG-1162587192
vm-1185303510 VM running RG-1185303510
vm-1555300244 VM deallocated RG-1555300244
vm-210251813 VM running RG-210251813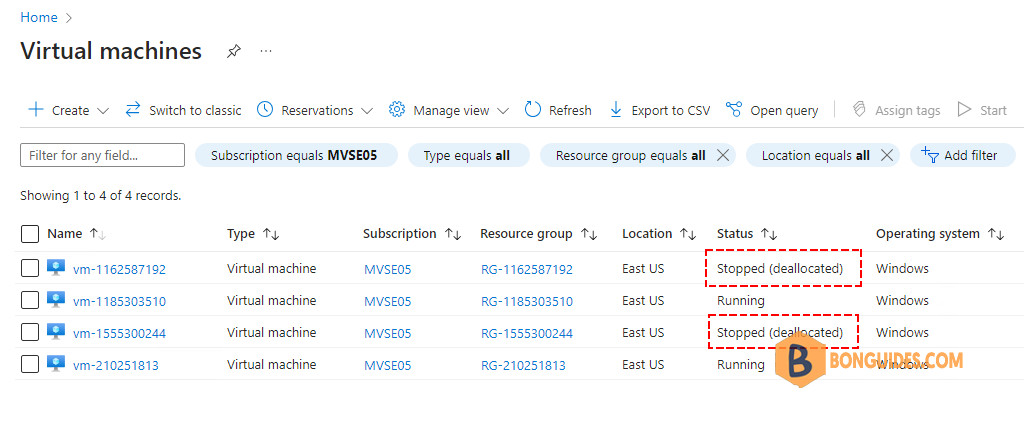
Not a reader? Watch this related video tutorial:





