Table of Contents
PowerShell is an advanced shell with integration of .NET objects. It’s more than just a replacement for the older cmd.exe. It can work with .NET assemblies, process large datasets, and even interact with web services.
Because of the .NET assemblies support, it can work with WinForms (or even WPF), making it possible to create scripts with GUIs.
System requirements
This has been tested to work with Windows PowerShell version 5.1. It’s likely going to work with older versions as well. But, because it depends on the .Net framework, so it’s not going to work with the new cross-platform PowerShell (there are no WinForms on Linux/macOS). You can check the version with
PS C:\> Get-Host | Select-Object version
Version
-------
5.1.22621.2506
PS C:\> Get-Host | Select-Object version
Version
-------
7.3.10Setting up the environment
Before we can start, let’s check a few things.
The first one is the script execution policy. It controls which scripts can be run. By default, Windows blocks execution of all scripts (more on that here).
We have to allow it to run local scripts that are not digitally signed. It’s possible to do this either by going through:
- Windows 10: Windows Settings > Updates & Security > For developers > Change execution policy.
- Windows 11: Windows Settings > For developers > PowerShell > Change execution policy.
Or just executing from administrator PowerShell.
Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSignedAnother (less important) thing is the code editor. Even though we could just write the entire script directly in PowerShell, it’s easier to use a full-featured editor with error-checking and syntax highlighting. Windows already comes with PowerShell ISE (Integrated Scripting Environment), but you can use Visual Studio Code with the PowerShell extension.
Writing a PowerShell script
Importing the assemblies
We have to import both System.Windows.Forms and System.Drawing assemblies. It’s possible to only include the first one but we also need the 2nd to specify control sizes.
Add-Type -AssemblyName System.Windows.Forms, System.DrawingYou can test it by creating a blank form:
Add-Type -AssemblyName System.Windows.Forms, System.Drawing
$form = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$form.ShowDialog()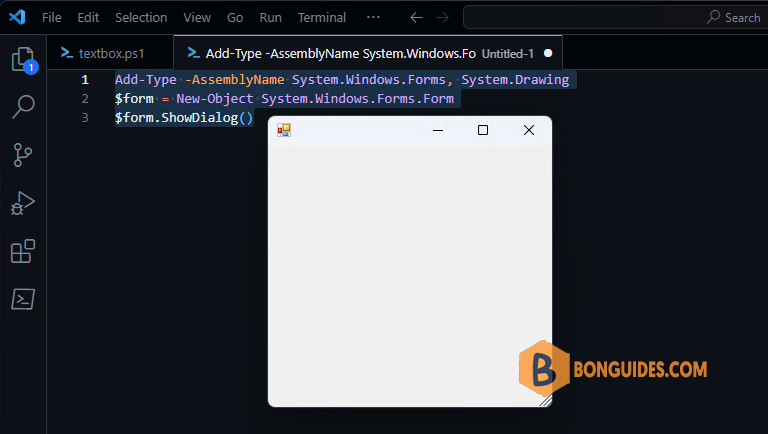
Adding controls
Let’s make a “Hello World” form. First, we create a top-level Form object:
Add-Type -AssemblyName System.Windows.Forms, System.Drawing
$form = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$form.ShowDialog()
$form = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$form.Text = "Some form"
$form.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(150, 145)
$form.AutoSize = $trueIn PowerShell, objects are created using New-Object. You can also pass parameters to constructors, similar to the new keyword in C#. Values are assigned to properties directly. Another difference is using $true instead of just true.
Let’s add a label and a button:
$label1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Label
$label1.Text = "Hello World!"
$label1.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point(30, 20);
$button = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button.Text = "Close"
$button.location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point(30, 60);
$button.DialogResult = [System.Windows.Forms.DialogResult]::OKThe $button.DialogResult line tells the form what to return when the button is clicked. You can use this to figure out whether the user clicked OK or Cancel. We also make $btn the default button and lay controls onto the form:
$form.AcceptButton = $button
$form.controls.Add($label1)
$form.controls.Add($button)All that’s left is showing the form itself:
$form.ShowDialog()Bring all parts together:
Add-Type -AssemblyName System.Windows.Forms, System.Drawing
$form = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$form.Text = "Some form"
$form.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(150, 145)
$form.AutoSize = $true
$label1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Label
$label1.Text = "Hello World!"
$label1.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point(30, 20);
$button = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button.Text = "Close"
$button.location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point(30, 60);
$button.DialogResult = [System.Windows.Forms.DialogResult]::OK
$form.AcceptButton = $button
$form.controls.Add($label1)
$form.controls.Add($button)
$form.ShowDialog()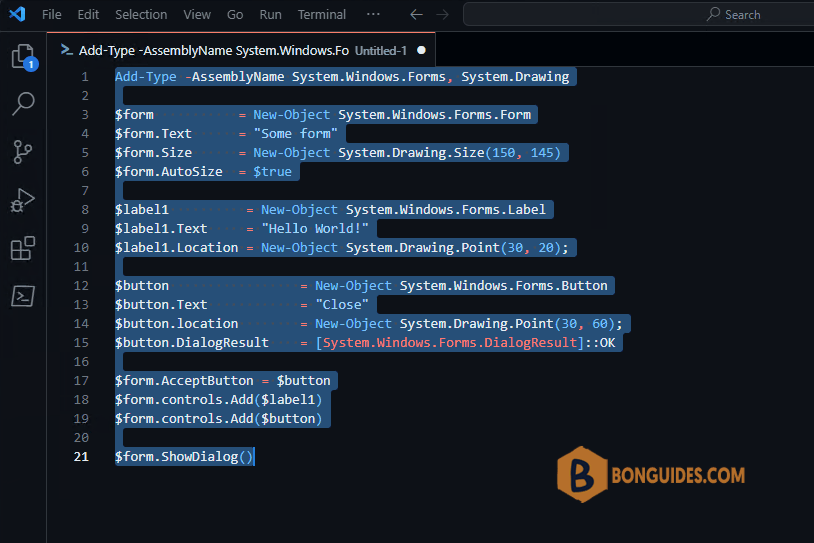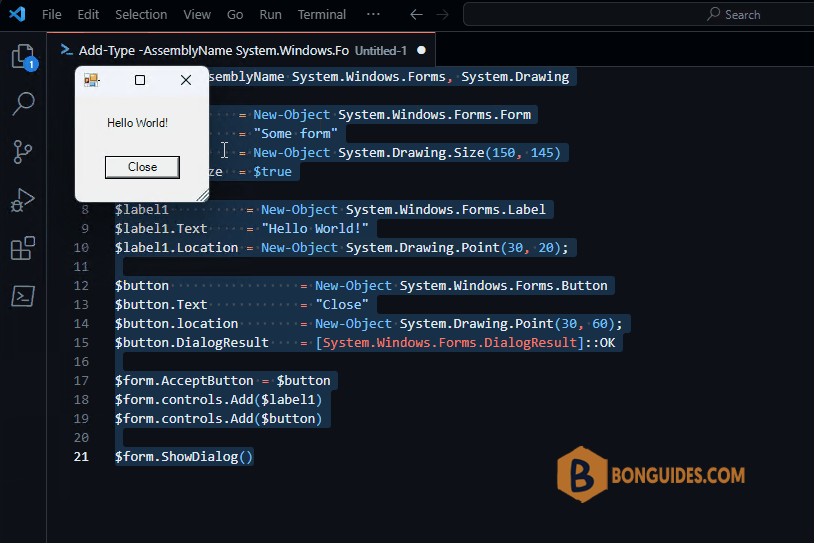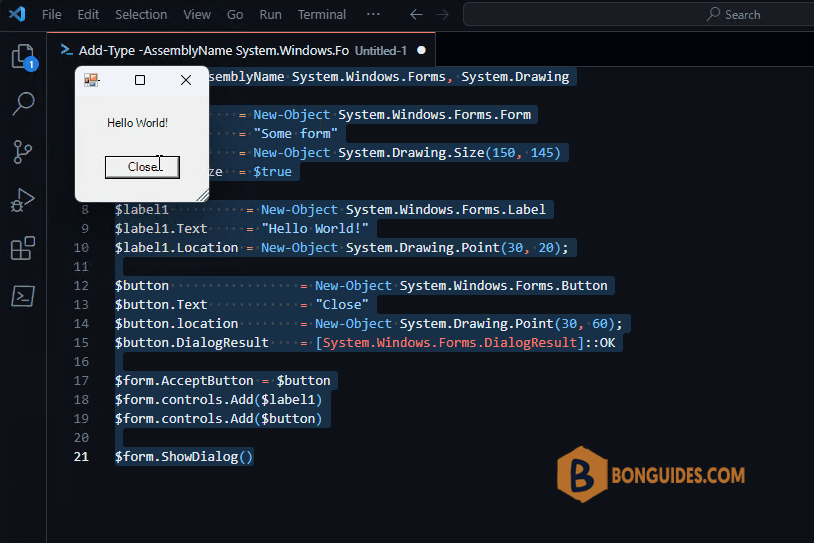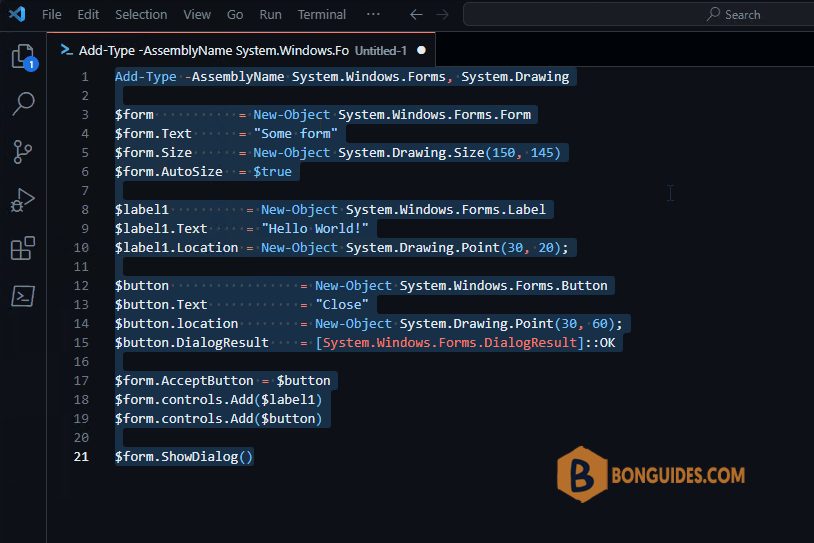
Event handlers
In our form, $button is the default OK button which just terminates the form. But we can use non-terminating event handlers as well. For example, let’s make it possible to click on the label:
$lable1.Add_Click({
[System.Windows.Forms.MessageBox]::Show("This is a lable!")
})You can call functions or scriptblocks from event handlers as you normally would.
Visual Styles
Sometimes, I’ve noticed with these GUI scripts is that different control styles are used when the script is run from the PowerShell console instead of VSCode. The console uses legacy rendering which falls back to using Windows 95-style controls. We need to enable Visual Styles to fix that:
[System.Windows.Forms.Application]::EnableVisualStyles()From here on, you can add more controls and event handlers.
The full script with GUI:
Add-Type -AssemblyName System.Windows.Forms, System.Drawing
[System.Windows.Forms.Application]::EnableVisualStyles()
$form = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Form
$form.Text = "Some form"
$form.Size = New-Object System.Drawing.Size(150, 145)
$form.AutoSize = $true
$label1 = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Label
$label1.Text = "Hello World!"
$label1.Location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point(30, 20);
$button = New-Object System.Windows.Forms.Button
$button.Text = "Close"
$button.location = New-Object System.Drawing.Point(30, 60);
$button.DialogResult = [System.Windows.Forms.DialogResult]::OK
$form.AcceptButton = $button
$form.controls.Add($label1)
$form.controls.Add($button)
$form.ShowDialog()



