Table of Contents
Check Windows Remote Management Configuration
The WinRM service is available in all modern Windows versions. In Windows Server it is enabled by default, but it is disabled in desktop Windows 11/10/8.1 editions. By default, the WinRM listener doesn’t accept remote connections. To check it, run the command below on a client:
WinRM enumerate winrm/config/listenerYou will see an error saying that the WinRM is not configured:
Enable Windows Remote Management WinRM
1. Right click on the Windows Start icon then select Windows PowerShell Admin or Windows Terminal Admin in Windows 11.
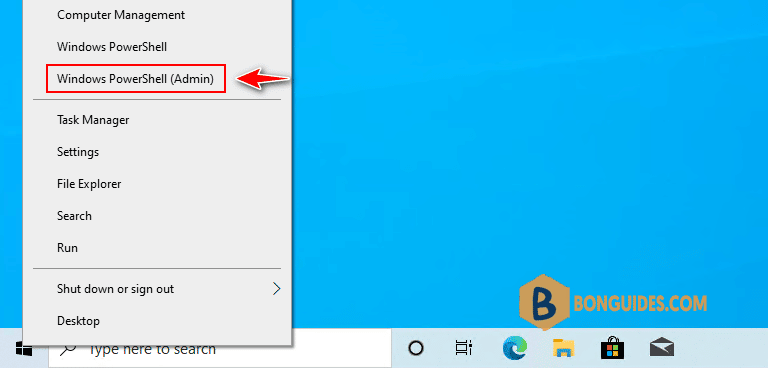
2. To enable and configure the WinRM service on Windows, let’s run this command:
winrm quickconfigPS C:\Windows\system32> winrm quickconfig
WinRM is not set up to receive requests on this machine.
The following changes must be made:
Start the WinRM service.
Set the WinRM service type to delayed auto start.
Make these changes [y/n]? y
WinRM has been updated to receive requests.
WinRM service type changed successfully.
WinRM service started.
WinRM is not set up to allow remote access to this machine for management.
The following changes must be made:
Enable the WinRM firewall exception.
Configure LocalAccountTokenFilterPolicy to grant administrative rights remotely to local users.
Make these changes [y/n]? y
WinRM has been updated for remote management.
WinRM firewall exception enabled.
Configured LocalAccountTokenFilterPolicy to grant administrative rights remotely to local users.This command will change the WinRM service startup type to automatic, apply default WinRM settings, and add exceptions for WinRM ports (TCP 5985 and 5986) to the list of exceptions in the Microsoft Defender Firewall.
PS C:\Users\admin> WinRM enumerate winrm/config/listener
Listener
Address = *
Transport = HTTP
Port = 5985
Hostname
Enabled = true
URLPrefix = wsman
CertificateThumbprint
ListeningOn = 10.10.230.10, 127.0.0.1Alternatively, you can use the following command to enable WinRM using PowerShell.
PS C:\Windows\system32> Enable-PSRemoting -Force
WinRM has been updated to receive requests.
WinRM service type changed successfully.
WinRM service started.
WinRM has been updated for remote management.
WinRM firewall exception enabled.
Configured LocalAccountTokenFilterPolicy to grant administrative rights remotely to local users.Enable WinRM via Group Policy
You can automatically enable and configure WinRM on domain computers using Windows GPO.
1. Open the Group Policy Management Console gpmc.msc, select an Active Directory container with the computers you want to enable WinRM on, and create a new GPO.
Open the policy to edit it
Go to Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Windows Settings -> Security Settings -> System Services. Find the Windows Remote Service (WS-Management) service and enable automatic startup for it
Then go to Computer Policies -> Preferences -> Control Panel Settings -> Services. Select New -> Service. Enter the service name WinRM, and select the Restart the Service action on the Recovery tab.
Go to Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Windows Remote Management (WinRM) -> WinRM Service. Enable Allow remote server management through WinRM. In the Ipv4/IPv6 filter box, you can specify IP addresses or subnetworks, on which WinRM connections must be listened to. If you want to allow WinRM connections on all IP addresses, leave * here.
Create Windows Defender Firewall rules allowing WinRM connections on the default ports TCP/5985 and TCP/5986. Go to Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Windows Settings -> Security Settings -> Windows Firewall with Advanced Security -> Windows Firewall with Advanced Security -> Inbound Rules. Select Windows Remote Management predefined rule.
Go to Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Windows Components -> Windows Remote Shell and enable Allow Remote Shell Access.
Update GPO settings on your clients and make sure that WinRM has been configured automatically. You can use the gpresult tool to troubleshoot Group Policy settings on client computers.
Checking WinRM Settings and PowerShell Connectivity
You may list the complete configuration of your WinRM service using this command:
winrm get winrm/configPS C:\Users\admin> Test-NetConnection -ComputerName 10.10.5.56 -Port 5985
ComputerName : 10.10.5.56
RemoteAddress : 10.10.5.56
RemotePort : 5985
InterfaceAlias : Ethernet
SourceAddress : 10.10.5.52
TcpTestSucceeded : TrueThen try to connect to a remote computer via WinRM. Open the PowerShell console and run the command below. If WinRM is enabled, the following response will appear:
PS C:\Users\admin> Test-WsMan 10.10.5.56
wsmid : http://schemas.dmtf.org/wbem/wsman/identity/1/wsmanidentity.xsd
ProtocolVersion : http://schemas.dmtf.org/wbem/wsman/1/wsman.xsd
ProductVendor : Microsoft Corporation
ProductVersion : OS: 0.0.0 SP: 0.0 Stack: 3.0You can check for an open WinRM port (TCP/5985) on the remote computer with PowerShell:
PS C:\Users\admin> Test-NetConnection -ComputerName 10.10.5.56 -Port 5985
ComputerName : 10.10.5.56
RemoteAddress : 10.10.5.56
RemotePort : 5985
InterfaceAlias : Ethernet
SourceAddress : 10.10.5.52
TcpTestSucceeded : TruePS C:\Users\admin> Enter-PSSession 10.10.5.56 -Credential (Get-Credential)
cmdlet Get-Credential at command pipeline position 1
Supply values for the following parameters:
Credential
[10.10.5.56]: PS C:\Users\admin\Documents>PS C:\> Invoke-Command -ComputerName 10.10.5.56 -ScriptBlock {ipconfig /all} -Credential (Get-Credential)
cmdlet Get-Credential at command pipeline position 1
Supply values for the following parameters:
Credential
Windows IP Configuration
Host Name . . . . . . . . . . . . : DESKTOP-9FDRHRJ
Primary Dns Suffix . . . . . . . :
Node Type . . . . . . . . . . . . : Hybrid
IP Routing Enabled. . . . . . . . : No
WINS Proxy Enabled. . . . . . . . : No
Ethernet adapter Ethernet0:
Connection-specific DNS Suffix . :
Description . . . . . . . . . . . : Intel(R) 82574L Gigabit Network Connection
Physical Address. . . . . . . . . : 00-0C-29-48-AA-0B
DHCP Enabled. . . . . . . . . . . : No
Autoconfiguration Enabled . . . . : Yes
Link-local IPv6 Address . . . . . : fe80::2539:e0f:b335:1987%8(Preferred)
IPv4 Address. . . . . . . . . . . : 10.10.5.56(Preferred)
Subnet Mask . . . . . . . . . . . : 255.255.0.0
Default Gateway . . . . . . . . . : 10.10.0.1
DHCPv6 IAID . . . . . . . . . . . : 100666409
DHCPv6 Client DUID. . . . . . . . : 00-01-00-01-29-D7-F4-C4-00-0C-29-48-AA-0B
DNS Servers . . . . . . . . . . . : 1.1.1.1
8.8.8.8
NetBIOS over Tcpip. . . . . . . . : Enabled




