Table of Contents
The Windows Server 2019 image is available in Microsoft Azure and you can create a Windows Server 2019 VM in Azure. Windows Server 2019 is also available on Azure Virtual Desktop.
The steps to create a Windows Server 2019 VM in Azure are easy and similar to that of Windows Server 2016. You can also create Azure Virtual Machine using the Cloud Shell in Azure portal. However, I prefer creating a new VM from the Azure portal over the cloud shell method.
Create a Windows Server 2019 VM in Azure Portal
1. You can try the following steps to create a Windows Server 2019 VM in Azure:
- Sign in to the Azure portal at https://portal.azure.com.
- Click Create a resource then select Virtual Machine.
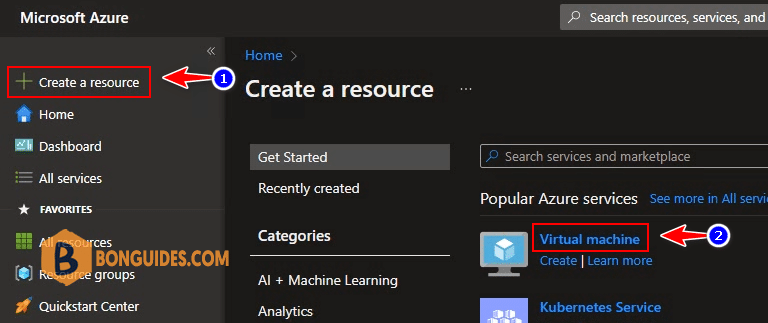
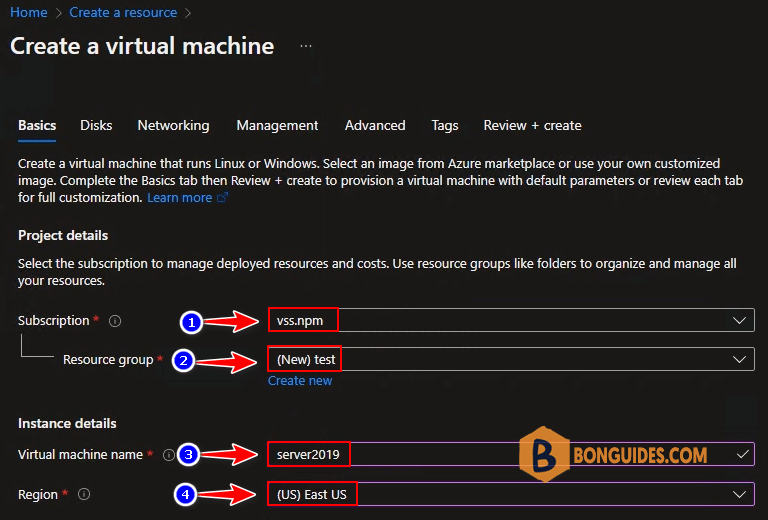
2. On the Create a virtual machine window, select the following.
- Subscription – Select your Azure subscription.
- Resource Group – Select the Azure resource group for Windows Server 2019 VM or you can create a new one.
- Virtual Machine Name – Specify the VM name. This will be the computer name after you image VM with Windows Server 2019.
- Region – Select the region.
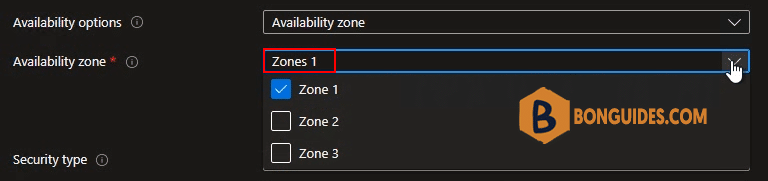
3. Availability options: Selecting multiple zones will create one VM per zone.
4. Image – Select the drop-down and select Windows Server 2019 as image. If you don’t see the Windows Server 2019 option, then select See all images.
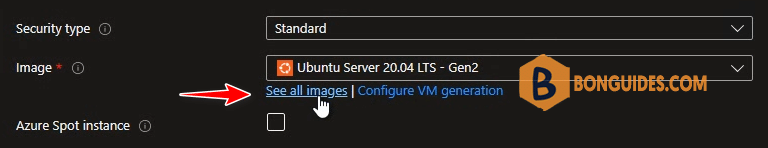
5. On the Marketplace window, type Windows Server 2019 as the search term and press Enter key. From the results, select Windows Server 2019 and now select Windows Server 2019 edition. I am going to select Windows Server 2019 Datacenter here.

6. Size: You can custom VM size to increase or reduce RAM and CPU for the VM.
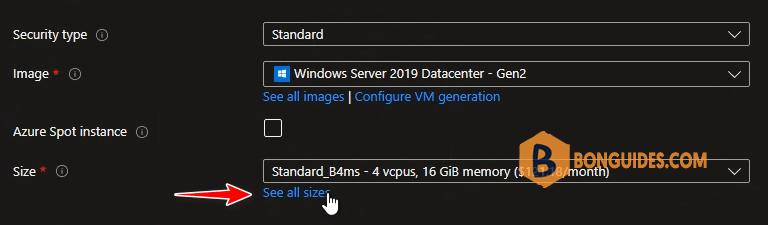
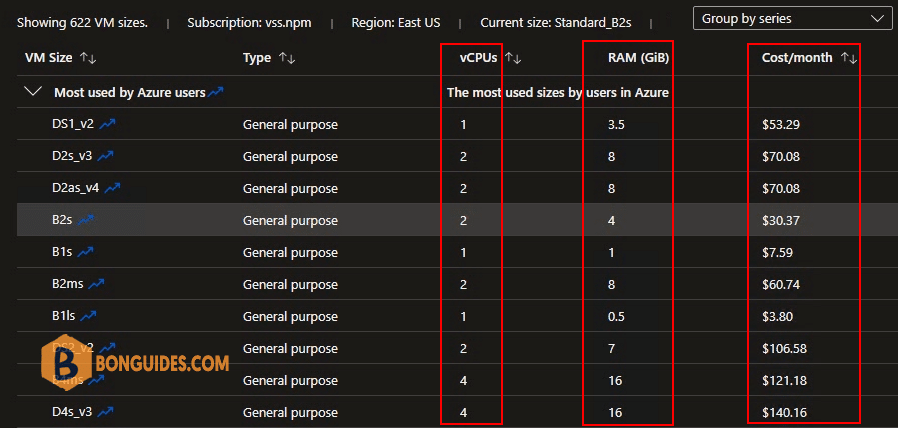
7. Select VM Size as you need, depending on RAM, CPU and Cost.
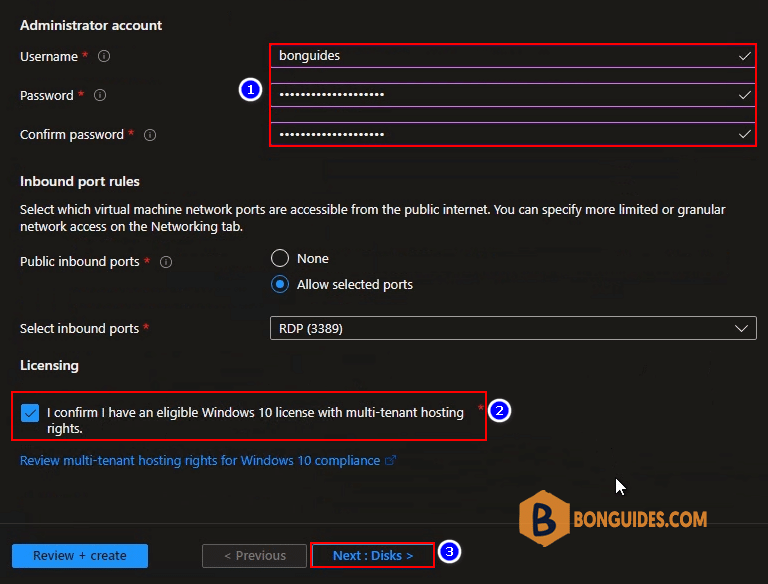
8. After you select Windows Server 2019 edition, you should specify the Administrator account details. You cannot use Administrator as username, so specify another name for Administrator.
Since you’re going to use this Windows Server 2019 VM for your work, you have to confirm if you have an eligible Windows Server 2019 license with multi-tenant hosting. Check that box to confirm the license and click Disk.
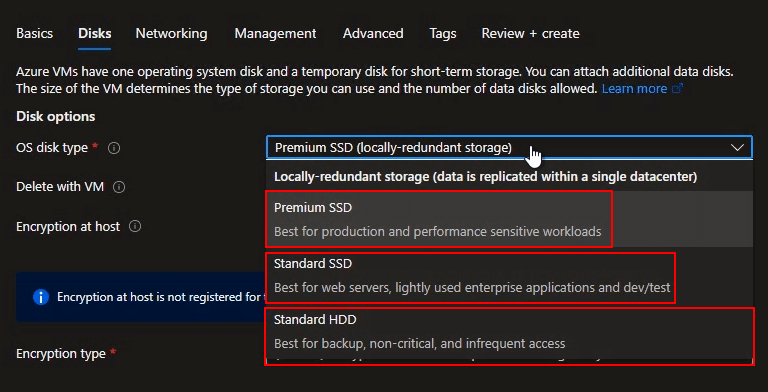
9. Select OS disk type: You can select Premium SSD, Stardard SSD or Standard HDD.
| Premium SSD | Standard SSD | Standard HDD | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Disk type | SSD | SSD | HDD |
| Scenario | Production and performance sensitive workloads | Web servers, lightly used enterprise applications and dev/test | Backup, non-critical, infrequent access |
| Max disk size | 32,767 GiB | 32,767 GiB | 32,767 GiB |
| Max throughput | 900 MB/s | 750 MB/s | 500 MB/s |
| Max IOPS | 20,000 | 6,000 | 2,000 |
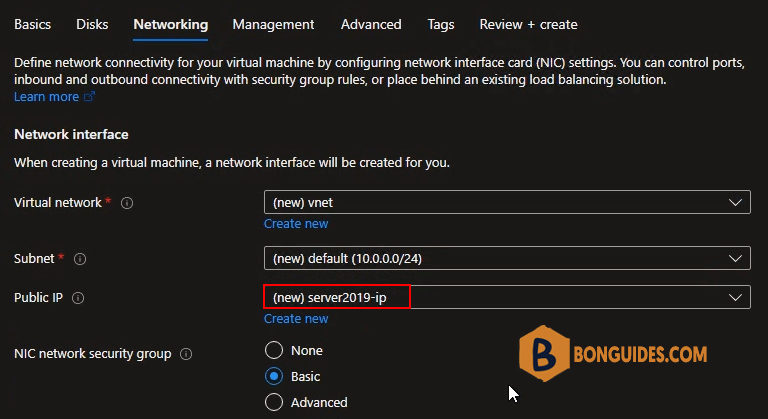
10. Network configuration: By default, an IP public will created with the VM.
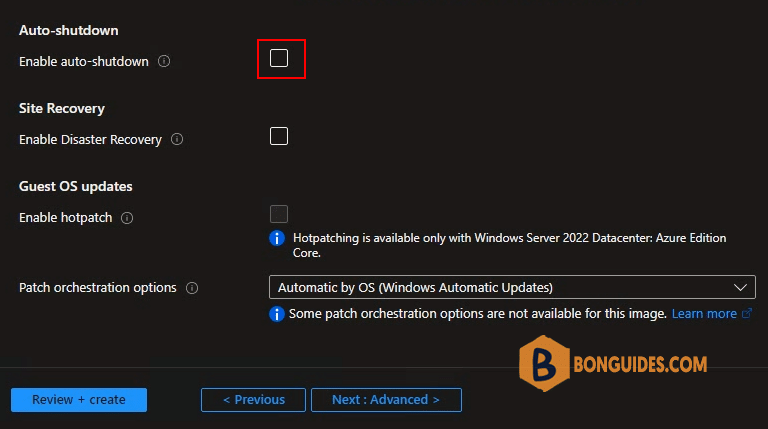
11. Management: Disable auto-shutdown feature by uncheck the checkbox.
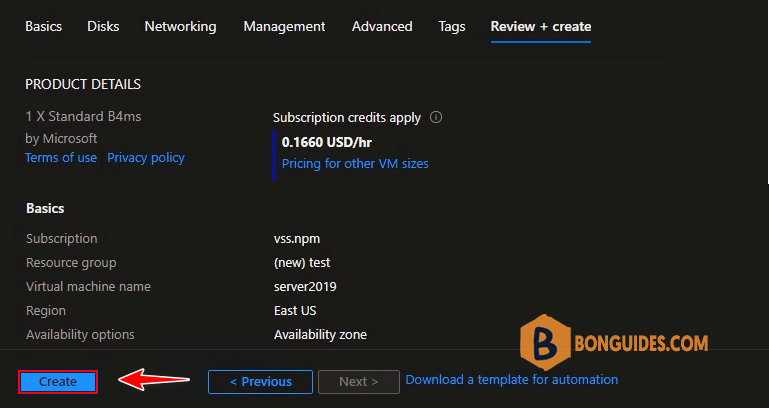
12. Once you see Validation passed, create the Windows Server 2019 virtual machine by selecting button.
13. The Windows Server 2019 Virtual Machine is now being created. You see the status as deployment is in progress. Wait for a few minutes while the VM is created.

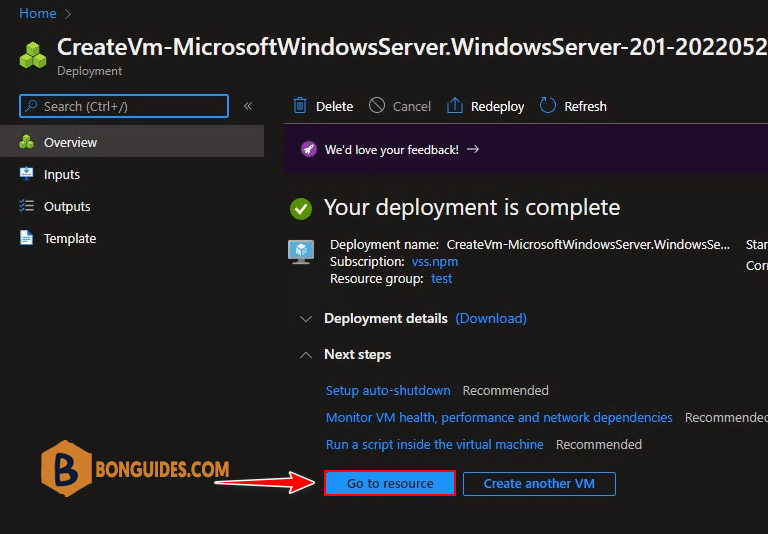
14. Your Deployment is complete – Congratulations, you have successfully created Windows Server 2019 VM in Azure. From the same screen, you can download deployment details. Select Go to Resource.
Connect to Windows Server 2019 VM in Azure using RDP
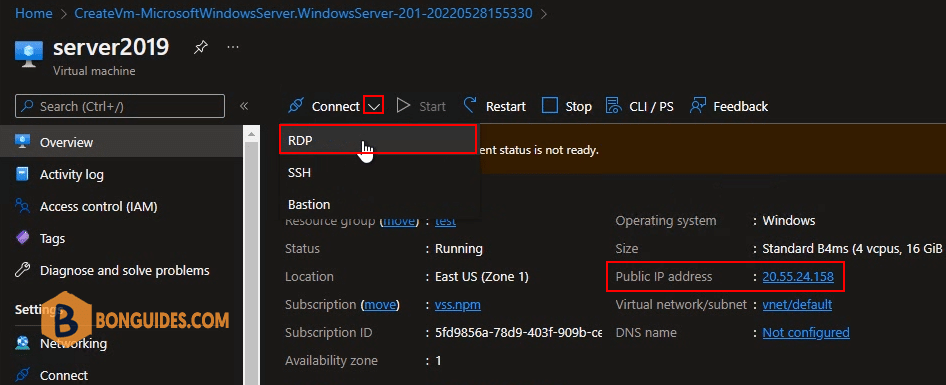
15. Once you create a Windows Server 2019 VM in Azure, you can connect to the virtual machine and access it via RDP (3389) using IP Public. On the Windows Server 2019 resource window, select Connect then select RDP.
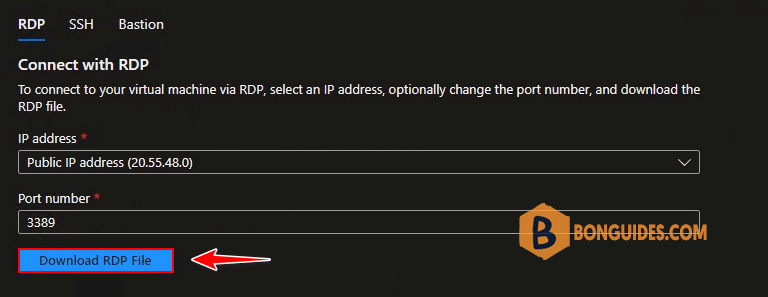
16. You should now see the public IP address of your Windows Server 2019 VM and port number (by default 3389). To connect to your virtual machine via RDP select Download RDP File.
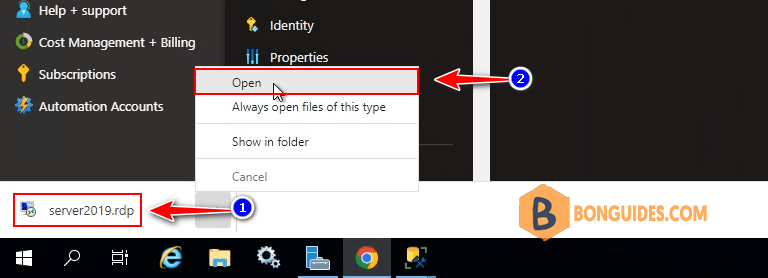
17. Open downloaded file then connect to your Windows Server 2019 VM using the credential that you’ve created in previous step.
Finally, your Windows Server 2019 VM is ready in minutes.