Table of Contents
Overview
Before we get started, I want to cover the two ways that SQL Server authenticates logins. The two ways are:
- Windows Authentication Mode.
- Windows and SQL Server Authentication Mode (Mixed Mode).
Windows Authentication Mode: In Windows authentication mode, we can only use Windows logins to connect to SQL Server. Windows Authentication utilizes the Kerberos security protocol .In enterprise environments, Windows login credentials are normally Active Directory domain credentials
Mixed Mode Authentication: In Mixed mode authentication, we can use either Windows authentication or SQL Server authentication to connect to SQL Server. Windows Authentication Mode is much more secure than Mixed Mode. SQL Server Authentication is provided for backward compatibility only. Whenever possible use Windows Authentication.
Checking SQL Server Authentication Mode using SSMS
1. Open SQL Management Studio then connect to a database instance.
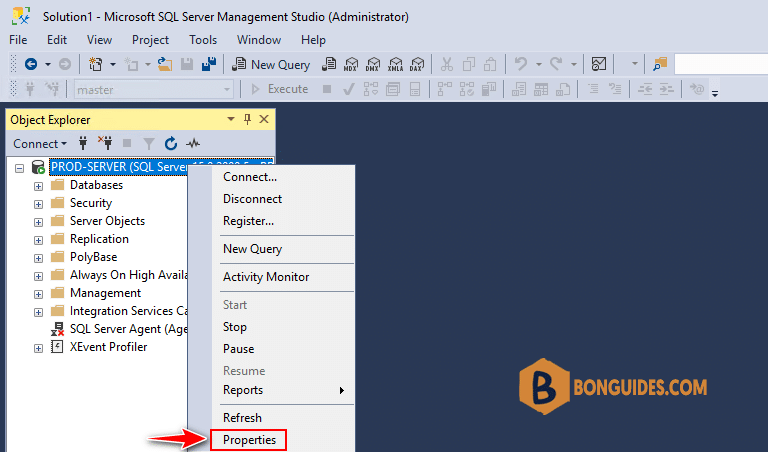
2. In SQL Server Management Studio Object Explorer, right-click on the server name, click Properties.
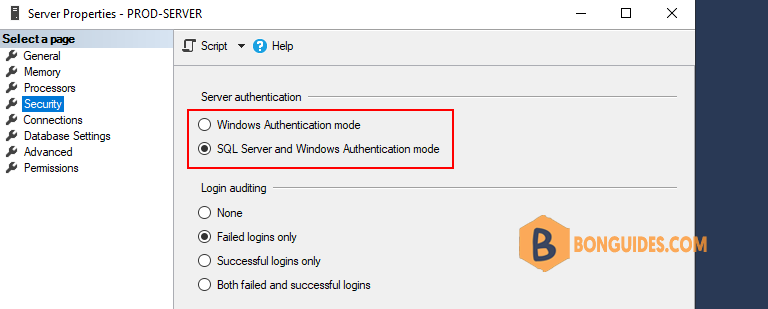
3. Select Security page to check the SQL Server Authentication. In this case we can see that it is Mixed Mode.
Checking Authentication Mode Using xp_instance_regread
Using xp_instance_regread system procedure, we can read the registry value. SQL Server stores a “1” for Windows Authentication and a “2” for SQL Server authentication (Mixed Mode) in the windows registry. You can execute the below query to check the SQL Server Authentication.
DECLARE @AuthenticationMode INT
EXEC master.dbo.xp_instance_regread N'HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE',
N'Software\Microsoft\MSSQLServer\MSSQLServer',
N'LoginMode', @AuthenticationMode OUTPUT
SELECT CASE @AuthenticationMode
WHEN 1 THEN 'Windows Authentication'
WHEN 2 THEN 'Windows and SQL Server Authentication'
ELSE 'Unknown'
END as [Authentication Mode] 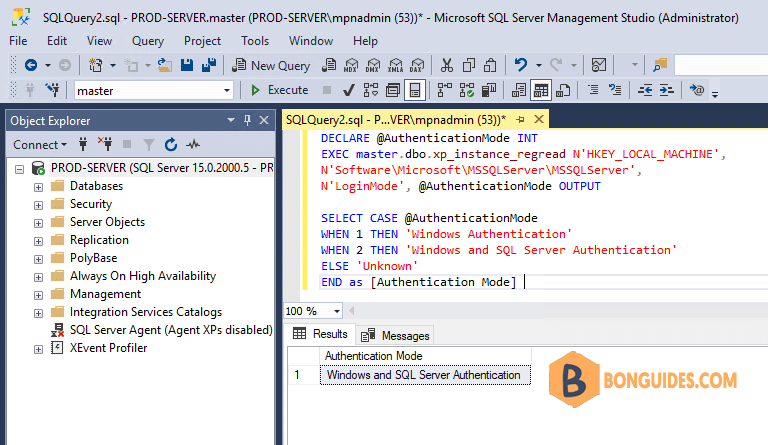
Checking Authentication Mode Using Server Property
The Server Property function will return “1” for Windows authentication and “0” for Windows/SQL Authentication (Mixed Mode). It would be nice if these values were consistent from what is stored in the registry.
SELECT CASE SERVERPROPERTY('IsIntegratedSecurityOnly')
WHEN 1 THEN 'Windows Authentication'
WHEN 0 THEN 'Windows and SQL Server Authentication'
END as [Authentication Mode] 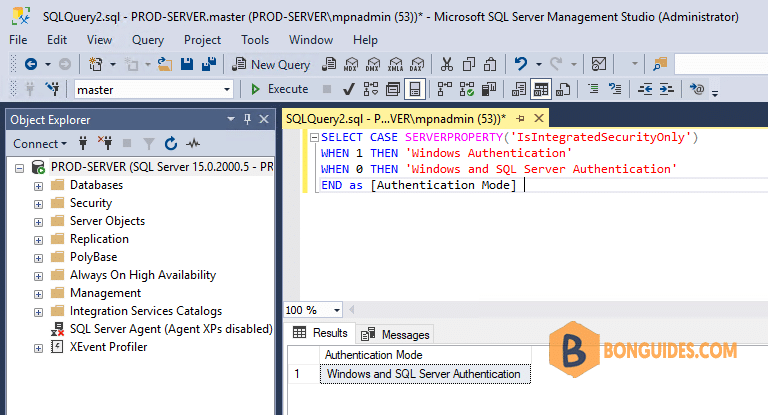
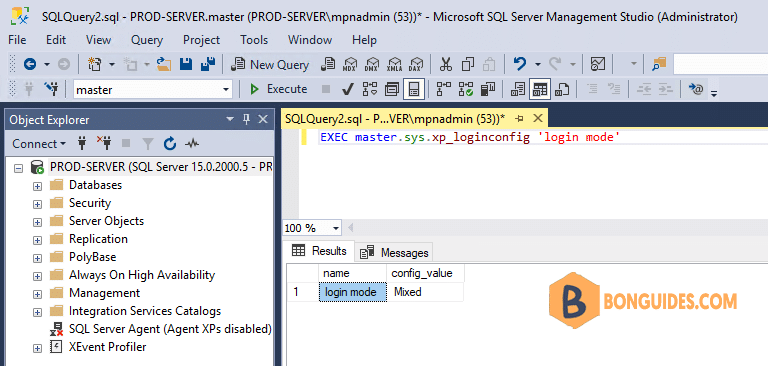
Checking Authentication Mode Using xp_logininfo
EXEC master.sys.xp_loginconfig 'login mode'