Table of Contents
What is a Microsoft Graph scope?
For many admins, the use of Scopes is a new addition to Office 365 PowerShell. The Scopes parameter was introduced with the Microsoft Graph PowerShell API, but the concept of Scopes is actually part of the OAuth2 specification.
PS C:\> Connect-MgGraph
Welcome To Microsoft Graph!The use of Scopes limits the user permissions available to an application or session.
By configuring Scopes when connecting to the Microsoft Graph PowerShell API, you effectively limit what permissions are available for the execution of commands. We’ll see this in a live example further down.
Connecting to MS Graph With Scopes
For example, you want to run a script that exports some user information from the Microsoft 365 Graph. Since you’ll only be reading user information, it makes good sense to limit your permissions to read-only (principle of least privilege).
Connect-MgGraph -Scopes "User.Read.All"This will ensure that you don’t accidentally make updates to user accounts. Also, it protects you from a rogue application trying to make changes when it should only be reading information. This will cause OAuth2 authentication to kick in (unless you have already consented to the permissions requested in the Scopes parameter):
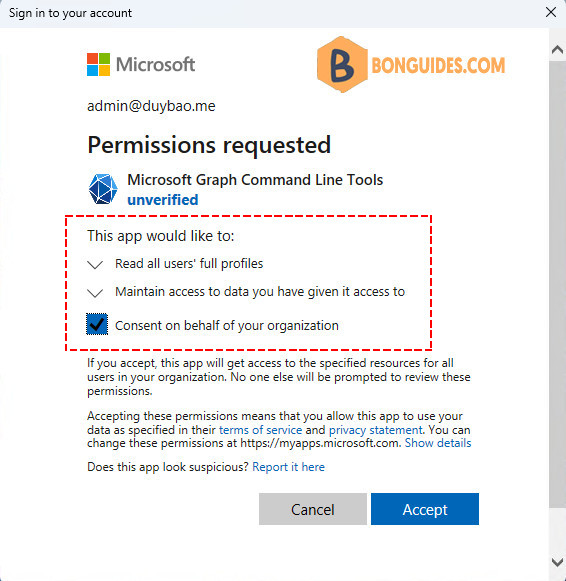
Notice that you can clearly see what permissions you’re allowing the Microsoft Graph PowerShell application to use. In this case, the app only has read permissions to all accounts.
After you accept the permissions request, the Microsoft Graph PowerShell application is configured with the new consent. Go to Enterprise Applications > Microsoft Graph Command Line Tools > Permissions > User consent to see it:
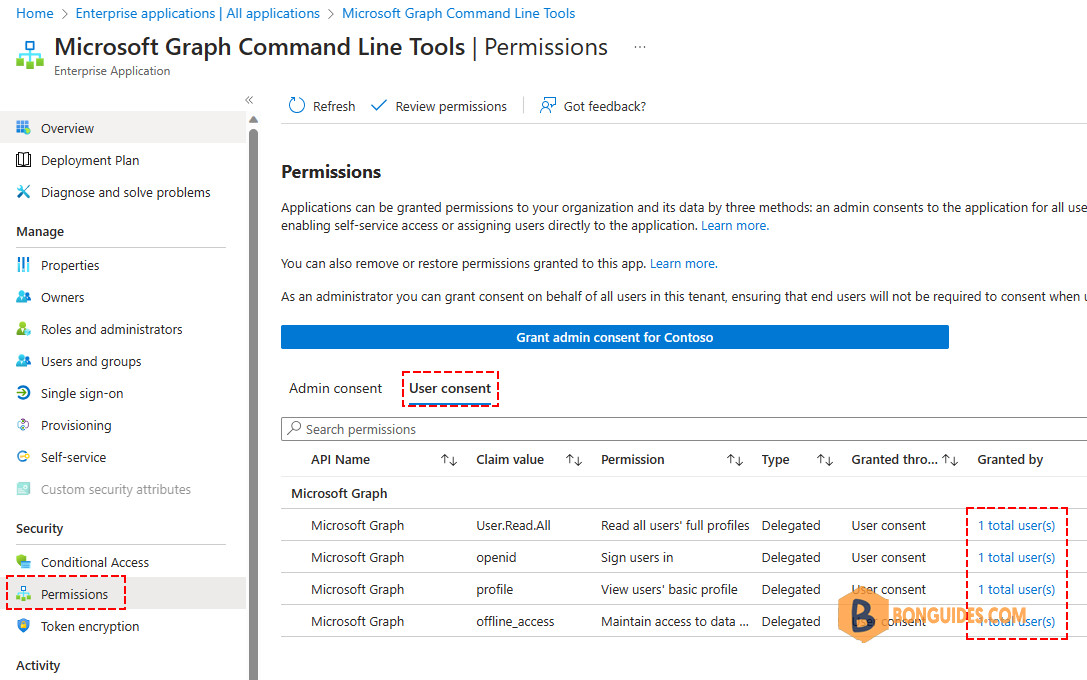
When you’ve connected to Microsoft Graph, you can check the current permission is granted for the current session by using the Get-MgContext cmdlet:
PS C:\> (Get-MgContext).scopes
openid
profile
User.Read.All
emailTo illustrate the protection received by using scopes configuration, let’s try to update an Entra ID user account by setting the UsageLocation attribute. We connect with Scopes set to User.Read.All and as expected, this fails:
PS C:\> Get-MgUser -UserId [email protected] -Property DisplayName,UsageLocation
DisplayName UsageLocation
----------- -------------
Alex Wilber US
PS C:\> Update-MgUser -UserId [email protected] -UsageLocation "UK"Update-MgUser : Insufficient privileges to complete the operation.
Status: 403 (Forbidden)
ErrorCode: Authorization_RequestDenied
Date: 2023-08-21T00:26:06
Headers:
Transfer-Encoding : chunked
…
To fix this we have to reconnect using a more extensive scope. With the new scope, you can now the write permission on all user accounts on your tenant.
Connect-MgGraph -Scopes "User.ReadWrite.All"Assuming we haven’t previously consented to this, we receive a new OAuth2 authentication dialog stating the new level of consent. This time, the app requires the read and write permission.
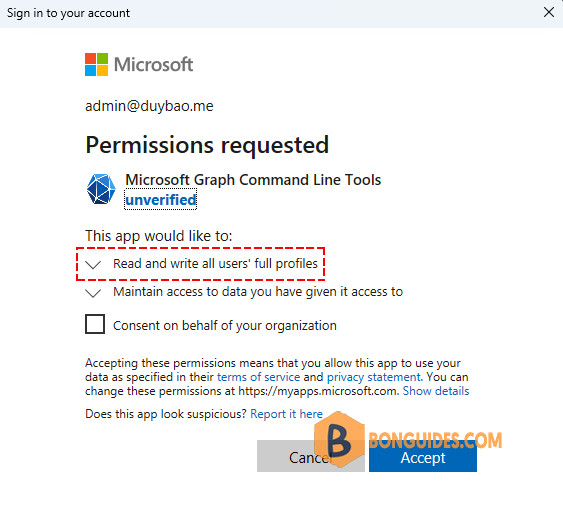
Once connected, when you check the MgContext, the new permission should be added.
PS C:\> (Get-MgContext).Scopes
openid
profile
User.Read.All
email
User.ReadWrite.AllAfter accepting this, the User consent of the Microsoft Graph PowerShell Enterprise Application is updated with the new consent which we can verify in the Azure Portal:
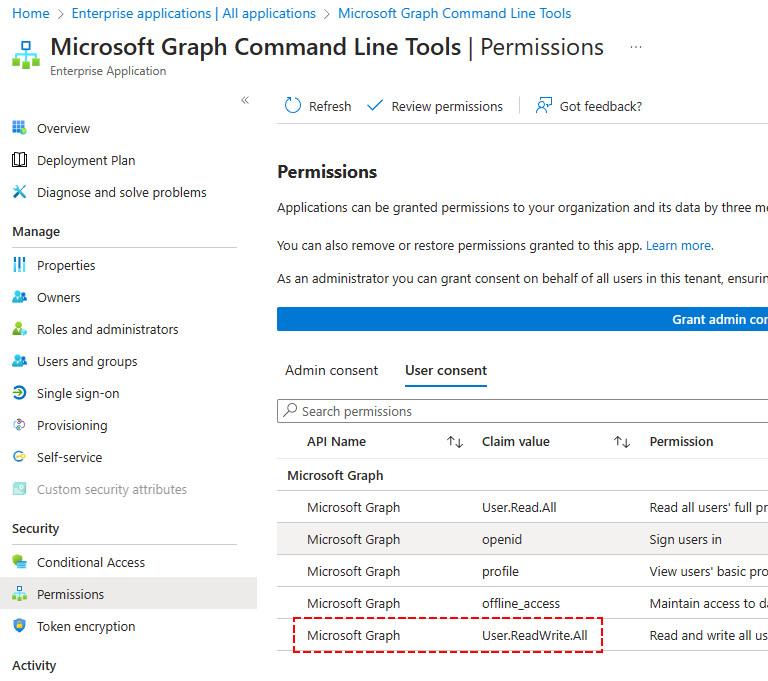
With the new scope in place, we are now able to write new information to user objects in Entra ID:
PS C:\> Update-MgUser -UserId [email protected] -UsageLocation "VN"
PS C:\> Get-MgUser -UserId [email protected] -Property DisplayName,UsageLocation
DisplayName UsageLocation
----------- -------------
Alex Wilber VNPS C:\> (Find-MgGraphCommand -Command 'New-MgDomain').Permissions
Name IsAdmin Description
---- ------- -----------
Domain.ReadWrite.All True Read and write domainsFinding Microsoft Graph Scopes
Finding the right scope can be a bit challenging at the beginning. But there are some good sources that you can use to determine which scopes you will need to specify:
- Microsoft Graph Explorer: https://developer.microsoft.com/en-us/graph/graph-explorer
- Microsoft Graph Rest API Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/graph/api/overview
- Find-MgGraphCommand, Find-MgGraphPermission cmdlets.
Microsoft Graph Explorer
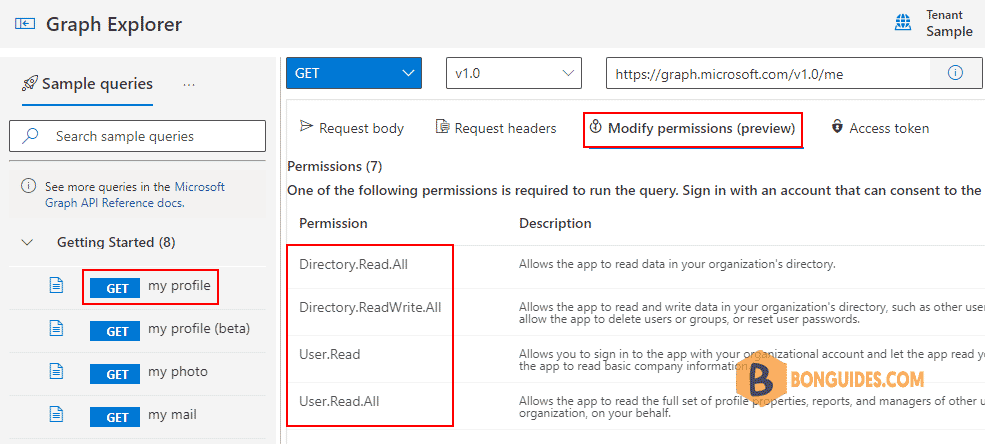
The Microsoft Graph Explorer is a great tool to test out API calls to Microsoft Graph. It comes with a lot of examples calls to help you get started. But it will also list the required permission for the call.
Open the Graph Explorer | Select an Sample Query on the left side | Click Modify Permissions tab.
Microsoft Graph Rest API Reference
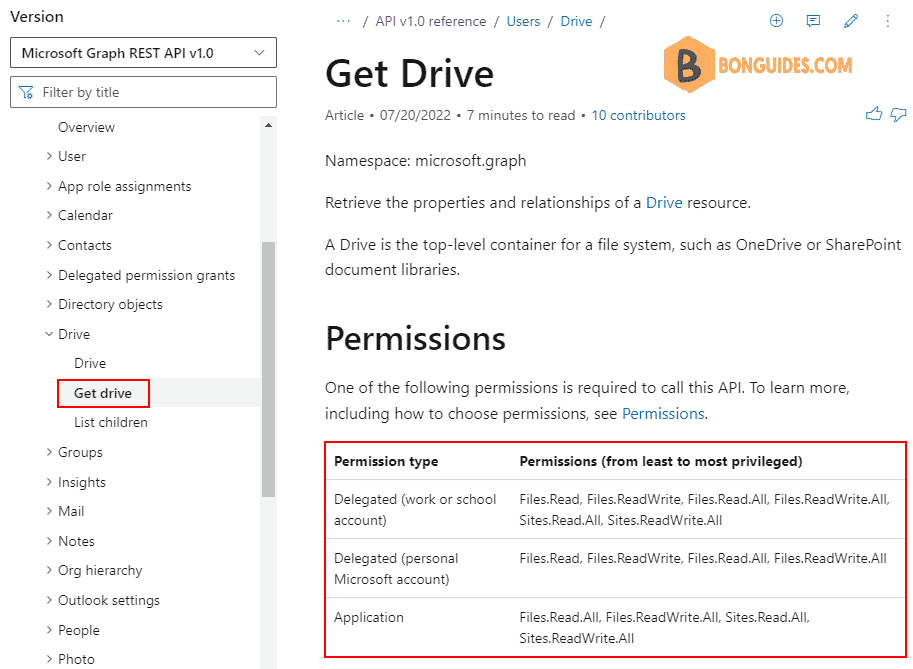
The other option is to use the Rest API Reference. You can select in the left menu one of the entities that you want to work with and then view the required permissions. You don’t need to add all scope, they are listed from least to most privileged.
An example, we find the scope to get OneDrive for Business for users.
Find-MgGraphCommand
Our favorite way to find the right scopes to connect to Microsoft Graph PowerShell is using Find-MgGraphCommand cmdlet.
For example, we found the right permission to update users’ information with Update-MgUser cmdlet.
(Find-MgGraphCommand -Command 'Update-MgUser').PermissionsName IsAdmin Description
---- ------- -----------
DeviceManagementApps.ReadWrite.All True Read and write Microsoft Intune apps
DeviceManagementConfiguration.ReadWrite.All True Read and write Microsoft Intune Device
DeviceManagementManagedDevices.ReadWrite.All True Read and write Microsoft Intune devices
DeviceManagementServiceConfig.ReadWrite.All True Read and write Microsoft Intune configuration
Directory.ReadWrite.All True Read and write directory data
User.EnableDisableAccount.All True Enable and disable user accounts
User.ManageIdentities.All True Manage user identities
User.ReadWrite False Read and update your profile
User.ReadWrite.All False Read and write all users' full profilesFind the required permissions to create a new user using Microsoft Graph.
PS C:\> (Find-MgGraphCommand -Command 'New-MgUser').Permissions
Name IsAdmin Description
---- ------- -----------
DeviceManagementApps.ReadWrite.All True Read and write Microsoft Intune apps
DeviceManagementConfiguration.ReadWrite.All True Read and write Microsoft Intune Device
DeviceManagementManagedDevices.ReadWrite.All True Read and write Microsoft Intune devices
DeviceManagementServiceConfig.ReadWrite.All True Read and write Microsoft Intune
Directory.ReadWrite.All True Read and write directory data
User.ReadWrite.All True Read and write all users' full profilesFind the permissions to create or add a new domain into Microsoft 365 tenant using Microsoft Graph.
PS C:\> (Find-MgGraphCommand -Command 'New-MgDomain').Permissions
Name IsAdmin Description
---- ------- -----------
Domain.ReadWrite.All True Read and write domainsThe required permissions to create a new Teams group.
PS C:\> (Find-MgGraphCommand -Command 'New-MgTeam').Permissions
Name IsAdmin Description
---- ------- -----------
Directory.ReadWrite.All True Read and write directory data
Group.ReadWrite.All True Read and write all groups
Team.Create False Create teamsThe permission to get the list of devices in your organization.
PS C:\> (Find-MgGraphCommand -Command 'Get-MgDevice').Permissions
Name IsAdmin Description
---- ------- -----------
Device.Read.All True Read all devices
Directory.Read.All True Read directory data
Directory.ReadWrite.All True Read and write directory dataThe permissions need to be assigned to get the list of Teams groups in your tenant.
PS C:\> (Find-MgGraphCommand -Command 'Get-MgTeam').Permissions
Name IsAdmin Description
---- ------- -----------
Directory.Read.All True Read directory data
Directory.ReadWrite.All True Read and write directory data
Group.Read.All True Read all groups
Group.ReadWrite.All True Read and write all groups
Team.ReadBasic.All False Read the names and descriptions of teams
TeamSettings.Read.All True Read teams' settings
TeamSettings.ReadWrite.All True Read and change teams' settingsAdditionally, you can use another Microsoft Graph PowerShell cmdlet to get the needed permissions to perform actions. Read more: How to Use Find-MgGraphPermission cmdlet in Microsoft Graph PowerShell
Not a reader? Watch this related video tutorial: